Explore the Family Name Yang
How common is the last name Yang in the United States?
Based on the Decennial U.S. Census data, the surname Yang has seen a significant increase in popularity over the past decade. In 2000, Yang was the 397th most common surname, whereas by 2010 it had climbed to the 290th position, marking an impressive rise of 26.95%. The count of people bearing the surname also increased from 72,627 in 2000 to 106,033 in 2010, a growth of 46%. Consequently, the proportion of individuals with this surname per 100,000 people also rose from 26.92 to 35.95 during the same period, reflecting a change of 33.54%.
| 2000 | 2010 | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | #397 | #290 | 26.95% |
| Count | 72,627 | 106,033 | 46% |
| Proportion per 100k | 26.92 | 35.95 | 33.54% |
Race and Ethnicity of people with the last name Yang
The ethnic identity associated with the surname Yang, according to the Decennial U.S. Census data, is primarily Asian/Pacific Islander. In 2000, 95.03% of individuals with the surname were of this ethnicity, and this figure slightly increased to 96.81% by 2010, reinforcing the strong Asian/Pacific Islander connection. Meanwhile, there was a substantial decrease (-57.02%) in the percentage of individuals identifying as two or more races, from 3.49% in 2000 to 1.50% in 2010. The proportion of White and Hispanic individuals sharing the surname grew modestly, with increases of 8.42% and 28.57% respectively. The percentage of Black individuals with the surname Yang also saw a moderate increase of 53.85%, although they constitute a smaller group. American Indian and Alaskan Native representation among those with the surname experienced a 50% decrease, albeit from a very small base.
| 2000 | 2010 | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Asian/Pacific Islander | 95.03% | 96.81% | 1.87% |
| Two or More Races | 3.49% | 1.5% | -57.02% |
| White | 0.95% | 1.03% | 8.42% |
| Hispanic | 0.35% | 0.45% | 28.57% |
| Black | 0.13% | 0.2% | 53.85% |
| American Indian and Alaskan Native | 0.04% | 0.02% | -50% |
Yang ancestry composition
23andMe computes an ancestry breakdown for each customer. People may have ancestry from just one population or they may have ancestry from several populations. The most commonly-observed ancestry found in people with the surname Yang is Chinese, which comprises 80.3% of all ancestry found in people with the surname. The next two most common ancestries are Korean (8.7%) and Chinese Dai (3.0%). Additional ancestries include Manchurian & Mongolian, Vietnamese, British & Irish, French & German, and Indonesian, Thai, Khmer & Myanma.
Ready to learn more about your ancestry? Get the most comprehensive ancestry breakdown on the market by taking our DNA test. Shop 23andMe
| ANCESTRY BREAKDOWN | COMPOSITION |
|---|---|
| Chinese | 80.3% |
| Korean | 8.7% |
| Chinese Dai | 3.0% |
| Other | 8.0% |

Possible origins of the surname Yang
Your DNA provides clues about where your recent ancestors may have lived. Having many distant relatives in the same location suggests that you may all share common ancestry there. Locations with many distant relatives can also be places where people have migrated recently, such as large cities. If a large number of individuals who share your surname have distant relatives in a specific area, it could indicate a connection between your surname and that location, stemming from either recent ancestral ties or migration.
Based on 23andMe data, people with last name Yang have recent ancestry locations in China and Taiwan.
| RECENT ANCESTRY Location | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Guangdong, China | 40.90% |
| Jiangsu, China | 40.70% |
| Zhejiang, China | 40.40% |
| Shanghai, China | 40.30% |
| Shandong, China | 40.30% |
What Yang haplogroups can tell you
Haplogroups are genetic population groups that share a common ancestor on either your paternal or maternal line. These paternal and maternal haplogroups shed light on your genetic ancestry and help tell the story of your family.
The top paternal haplogroup of people with the surname Yang is O-F46, which is predominantly found among people with East Asian & Indigenous American ancestry. Haplogroup O-F46 is descended from haplogroup O-M1359. Other common haplogroups include O-F8 and O-CTS2498, which are predominantly found among people with East Asian & Indigenous American and East Asian & Indigenous American ancestry. Other surnames with similar common haplogroups are: Li, Chang, Zhang, Wang, Liu, Chen, Wu, Zhou, Lu, Xu.
The most common maternal haplogroups of people with Yang surname are: A4, B5a1, M7b. These most commonly trace back to individuals of East Asian & Indigenous American and European ancestry.
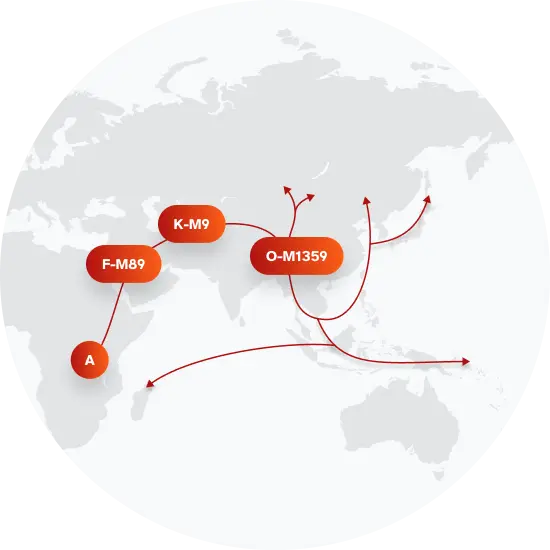 Paternal Haplogroup Origins O-M1359
Paternal Haplogroup Origins O-M1359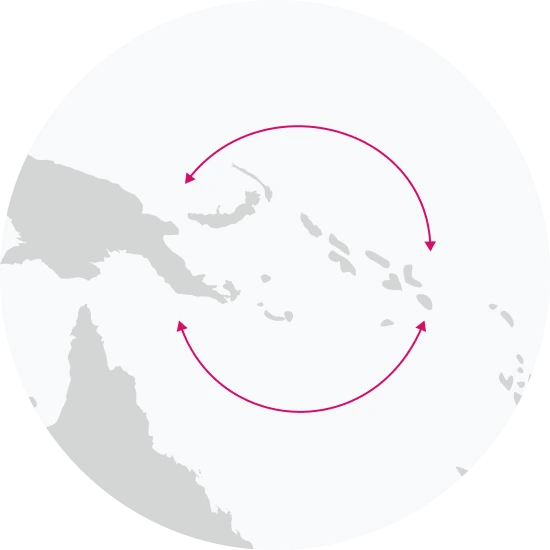
Your paternal lineage may be linked to many of the Massim groups of Papua New Guinea
Haplogroup O2a is prevalent among Massim ethnic groups, including the populations of Airara, Nomanby, the eastern tip of the mainland, the Trobriand Islands, Gawa, Woodlark, the Laughland Islands, and western Calvados. While Papua New Guinea has been inhabited for over 50,000 years, the Massim may have arrived in the last 2,000 years. Today, these populations remain connected through a traditional island trading system called the Kula Ring. Under this exchange system, residents ensure that goods that are only available on some islands, but that are vitally needed in other islands, are shared among the island populations. Only Massim men participate in the Kula exchange system, and it is common for men to be away from home for months at a time when trading with men from other islands.
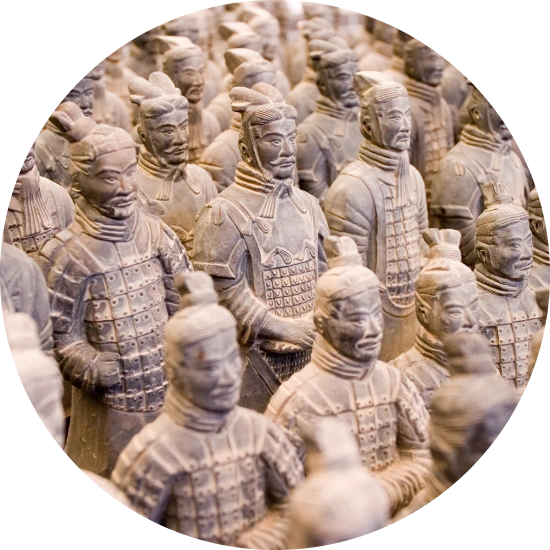
Your maternal lineage may be linked to the builders of the Terracotta Army
Qin Shi Huang, who unified warring states to become the First Emperor of China and founded the Qin Dynasty, ruled the Chinese state of Qin from 247 BC to 210 BC. In addition to his political feats, his reign is known for the massive construction projects, including his mausoleum in the Shaanxi province of central China, which began construction in 246 BC. To aid him in the afterlife, 8,000 perfectly life-like soldiers were crafted out of molds and clay and placed at guard over his tomb: his own Terracotta Army.An estimated 700,000 workers were involved in the mausoleum construction alone, and in 2003, hundreds of skeletal remains were unearthed near the mausoleum. Curious about the ethnic origins of these men, a group of Chinese scientists decided to examine their maternal haplogroups. They found that some of these workers belonged to haplogroup A, and that the group had come from a variety of places across East Asia.

What do people with the surname Yang have in common?
Spoiler alert: it's complicated. People with the same last name are usually no more genetically similar than a randomly sampled group of people from the same population. That said, people with the same surname are more likely to have similar ancestries than randomly sampled individuals. The reason is the tendency of people with similar cultural or geographical backgrounds to preferentially mate with one another. That's why people who share a surname may be more likely to share traits and tendencies in common than people within the general population. Check out the percentages below to see the prevalences of tastes, habits, and traits of people with your surname compared with prevalences among 23andMe users.
Preferences
Traits
Habits
Wellness
Are health conditions linked to the last name Yang?
The short answer is that, if there is an association between surname and health, it's usually more about your ancestry than your name. Individuals with a given surname are no more genetically similar than the general population but often have similar ancestries. The populations of people associated with those shared ancestries often have sets of genetic variations, also known as alleles, in common. Some of those alleles are associated with a greater likelihood of developing certain diseases.
Disease variant frequency by ancestry
Disease allele frequencies in populations associated with the surname Yang are shown below. Important Note: not everyone with a disease allele will develop these health condition