Explore the Family Name Yan
How common is the last name Yan in the United States?
Based on the Decennial U.S. Census, the popularity of the surname Yan has seen a significant increase between 2000 and 2010. In 2000, it was ranked as the 4091st most common surname, but by 2010, it had risen to the 3182nd position, indicating a positive change of 22.22%. The actual count of individuals with this surname also increased from 8,016 in 2000 to 11,354 in 2010, a substantial growth of 41.64%. This suggests an increasing number of people with the surname Yan, with the proportion per 100,000 people climbing by 29.63% over the decade.
| 2000 | 2010 | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | #4,091 | #3,182 | 22.22% |
| Count | 8,016 | 11,354 | 41.64% |
| Proportion per 100k | 2.97 | 3.85 | 29.63% |
Race and Ethnicity of people with the last name Yan
In terms of ethnic identity, the data from the Decennial U.S. Census shows that the majority of people with the surname Yan identify as Asian/Pacific Islander. From 2000 to 2010, the percentage of Yan's identifying with this ethnicity increased from 89.13% to 94.06%, a rise of 5.53%. Those identifying as having two or more races declined by 34.36%, while those identifying as white decreased by 51.39%. The proportion of Yan's identifying as Hispanic fell slightly by 9.52%. Lastly, those identifying as Black and American Indian and Alaskan Native were recorded as 0% in 2010; the previous data for these categories was suppressed for privacy reasons.
| 2000 | 2010 | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Asian/Pacific Islander | 89.13% | 94.06% | 5.53% |
| White | 6.11% | 2.97% | -51.39% |
| Hispanic | 1.47% | 1.33% | -9.52% |
| Two or More Races | 1.63% | 1.07% | -34.36% |
| Black | 1.53% | 0% | 0% |
| American Indian and Alaskan Native | 0.11% | 0% | 0% |
Yan ancestry composition
23andMe computes an ancestry breakdown for each customer. People may have ancestry from just one population or they may have ancestry from several populations. The most commonly-observed ancestry found in people with the surname Yan is Chinese, which comprises 82.9% of all ancestry found in people with the surname. The next two most common ancestries are Korean (3.0%) and Chinese Dai (2.8%). Additional ancestries include Manchurian & Mongolian, Vietnamese, Iranian, Caucasian & Mesopotamian, Filipino & Austronesian, and British & Irish.
Ready to learn more about your ancestry? Get the most comprehensive ancestry breakdown on the market by taking our DNA test. Shop 23andMe
| ANCESTRY BREAKDOWN | COMPOSITION |
|---|---|
| Chinese | 82.9% |
| Korean | 3.0% |
| Chinese Dai | 2.8% |
| Other | 11.4% |
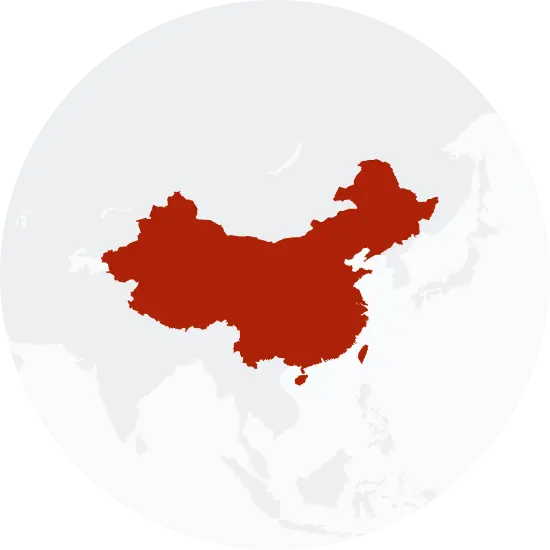

Possible origins of the surname Yan
Your DNA provides clues about where your recent ancestors may have lived. Having many distant relatives in the same location suggests that you may all share common ancestry there. Locations with many distant relatives can also be places where people have migrated recently, such as large cities. If a large number of individuals who share your surname have distant relatives in a specific area, it could indicate a connection between your surname and that location, stemming from either recent ancestral ties or migration.
Based on 23andMe data, people with last name Yan have recent ancestry locations all within China.
| RECENT ANCESTRY Location | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Guangdong, China | 36.20% |
| Shandong, China | 35.90% |
| Fujian, China | 35.90% |
| Jiangsu, China | 35.90% |
| Zhejiang, China | 35.70% |
What Yan haplogroups can tell you
Haplogroups are genetic population groups that share a common ancestor on either your paternal or maternal line. These paternal and maternal haplogroups shed light on your genetic ancestry and help tell the story of your family.
The top paternal haplogroup of people with the surname Yan is O-F8, which is predominantly found among people with East Asian & Indigenous American ancestry. Haplogroup O-F8 is descended from haplogroup O-M1359. Other common haplogroups include O-F46 and O-M307.1, which are predominantly found among people with East Asian & Indigenous American and East Asian & Indigenous American ancestry. Other surnames with similar common haplogroups are: Sun, Wang, Zhang, Li, Lu, Guo, Zhu, Wu, Gao, Zhao.
The most common maternal haplogroups of people with Yan surname are: F1a1, D4, M7b. These most commonly trace back to individuals of East Asian & Indigenous American and European ancestry.
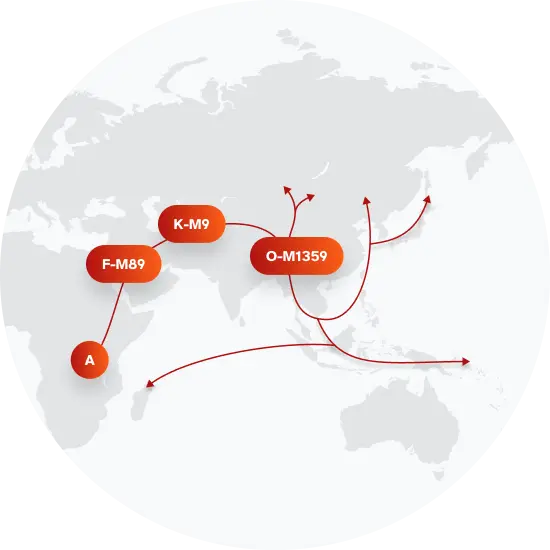 Paternal Haplogroup Origins O-M1359
Paternal Haplogroup Origins O-M1359
Your paternal lineage may be linked to the Han Chinese
Haplogroup O-Page23 has been found in several populations of the Han Chinese ethnic group. The ancestors of the Han, called the Huaxia, lived in the upriver basin of the Yellow River 5,000-6,000 years ago. As agricultural technology improved, the Huaxia spread east and south, and became the Han Chinese. Over the last 2,000 years, there have been three major migrations of the Han southward. The first of these migrations occurred during the Jin Dynasty from 317 to 420 CE, when nearly one million people moved south. A second migration occurred during the Tang Dynasty, after the An-Shi Rebellion, between 755 and 762 CE. The last migration occurred during the Southern Song Dynasty, from 1127 to 1297 CE, when nearly 5 million people migrated southward. The Pinghua, a branch of Han in which haplogroup O2a2b1a1 is particularly common, may be descendants of indigenous minority groups that adopted Han culture during one such major migration event.
Your maternal lineage may be linked to the Han
Members of haplogroup D are found in both northern and southern Han Chinese populations at low to moderate frequencies. The Han people, who all share the same language and similar cultural practices, are the largest ethnic group in the world, with about 1.2 billion people. Historical evidence shows that Han people are descendants of the ancient Huaxia tribes that come from northern China, and Han language and culture only expanded into southern China in the last 2,000 years. The spread of Han people and culture from northern to southern China was likely driven by warfare and famine in the north.

What do people with the surname Yan have in common?
Spoiler alert: it's complicated. People with the same last name are usually no more genetically similar than a randomly sampled group of people from the same population. That said, people with the same surname are more likely to have similar ancestries than randomly sampled individuals. The reason is the tendency of people with similar cultural or geographical backgrounds to preferentially mate with one another. That's why people who share a surname may be more likely to share traits and tendencies in common than people within the general population. Check out the percentages below to see the prevalences of tastes, habits, and traits of people with your surname compared with prevalences among 23andMe users.
Preferences
Traits
Habits
Wellness

Migraine
A severe headache characterized by intense pain, sensitivity to light and sound, and often accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
"Yan" Surname 6.8%
23andMe Users 16.4%
Are health conditions linked to the last name Yan?
The short answer is that, if there is an association between surname and health, it's usually more about your ancestry than your name. Individuals with a given surname are no more genetically similar than the general population but often have similar ancestries. The populations of people associated with those shared ancestries often have sets of genetic variations, also known as alleles, in common. Some of those alleles are associated with a greater likelihood of developing certain diseases.
Disease variant frequency by ancestry
Disease allele frequencies in populations associated with the surname Yan are shown below. Important Note: not everyone with a disease allele will develop these health condition









