Explore the Family Name Watanabe
How common is the last name Watanabe in the United States?
Based on the Decennial U.S. Census data, the popularity of the surname Watanabe has seen a slight decrease between 2000 and 2010. In 2000, Watanabe was the 5115th most popular surname, but by 2010 it had slipped to the 5605th position, marking a drop of 9.58%. The total count of people with this surname also decreased from 6295 in 2000 to 6204 in 2010, representing a 1.45% decline. This translated to a reduction in the proportion per 100,000 people from 2.33 to 2.1.
| 2000 | 2010 | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | #5,115 | #5,605 | -9.58% |
| Count | 6,295 | 6,204 | -1.45% |
| Proportion per 100k | 2.33 | 2.1 | -9.87% |
Race and Ethnicity of people with the last name Watanabe
The ethnicity distribution for the surname Watanabe saw some significant changes during the same period, as per the Decennial U.S. Census. The majority of Watanabes identified as Asian/Pacific Islander, although this percentage decreased slightly from 83.94% in 2000 to 79.40% in 2010. Conversely, those identifying with two or more races increased from 7.47% to 10.20%, a substantial rise of 36.55%. The percentage of Watanabes identifying as White also grew marginally from 6.39% to 6.85%. A noticeable increase was observed among those identifying as Hispanic, which surged from 1.97% to 3.37%, a growth of 71.07%. Meanwhile, there were no Watanabes who identified as Black or American Indian and Alaskan Native in 2010, compared to minimal percentages in 2000.
| 2000 | 2010 | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Asian/Pacific Islander | 83.94% | 79.4% | -5.41% |
| Two or More Races | 7.47% | 10.2% | 36.55% |
| White | 6.39% | 6.85% | 7.2% |
| Hispanic | 1.97% | 3.37% | 71.07% |
| Black | 0.14% | 0% | 0% |
| American Indian and Alaskan Native | 0.1% | 0% | 0% |
Watanabe ancestry composition
23andMe computes an ancestry breakdown for each customer. People may have ancestry from just one population or they may have ancestry from several populations. The most commonly-observed ancestry found in people with the surname Watanabe is Japanese, which comprises 70.6% of all ancestry found in people with the surname. The next two most common ancestries are British & Irish (10.1%) and French & German (5.3%). Additional ancestries include Filipino & Austronesian, Chinese, Spanish & Portuguese, Korean, and Vietnamese.
Ready to learn more about your ancestry? Get the most comprehensive ancestry breakdown on the market by taking our DNA test. Shop 23andMe
| ANCESTRY BREAKDOWN | COMPOSITION |
|---|---|
| Japanese | 70.6% |
| British & Irish | 10.1% |
| French & German | 5.3% |
| Other | 14.0% |
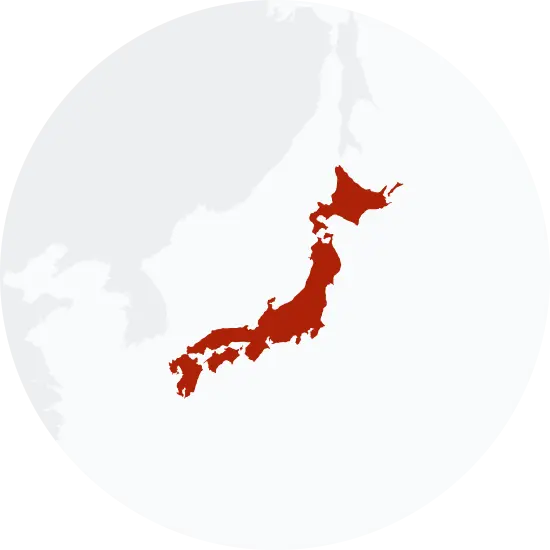
Possible origins of the surname Watanabe
Your DNA provides clues about where your recent ancestors may have lived. Having many distant relatives in the same location suggests that you may all share common ancestry there. Locations with many distant relatives can also be places where people have migrated recently, such as large cities. If a large number of individuals who share your surname have distant relatives in a specific area, it could indicate a connection between your surname and that location, stemming from either recent ancestral ties or migration.
Based on 23andMe data, people with last name Watanabe have recent ancestry locations in Japan and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
| RECENT ANCESTRY Location | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Hiroshima Prefecture, Japan | 63.90% |
| Okinawa Prefecture, Japan | 56.80% |
| Tokyo, Japan | 49.70% |
| Fukushima Prefecture, Japan | 26.80% |
| Kumamoto Prefecture, Japan | 24.00% |
What Watanabe haplogroups can tell you
Haplogroups are genetic population groups that share a common ancestor on either your paternal or maternal line. These paternal and maternal haplogroups shed light on your genetic ancestry and help tell the story of your family.
The top paternal haplogroup of people with the surname Watanabe is D-Z1504, which is predominantly found among people with East Asian & Indigenous American ancestry. Haplogroup D-Z1504 is descended from haplogroup D-M174. Other common haplogroups include O-CTS713 and D-M116.1, which are predominantly found among people with East Asian & Indigenous American and East Asian & Indigenous American ancestry. Other surnames with similar common haplogroups are: Yamamoto, Takahashi, Sato, Yoshida, Suzuki, Nakamura, Nawrocki, Duron, Durocher, Durfee.
The most common maternal haplogroups of people with Watanabe surname are: H, M7a1a, D4a1. These most commonly trace back to individuals of East Asian & Indigenous American and European ancestry.
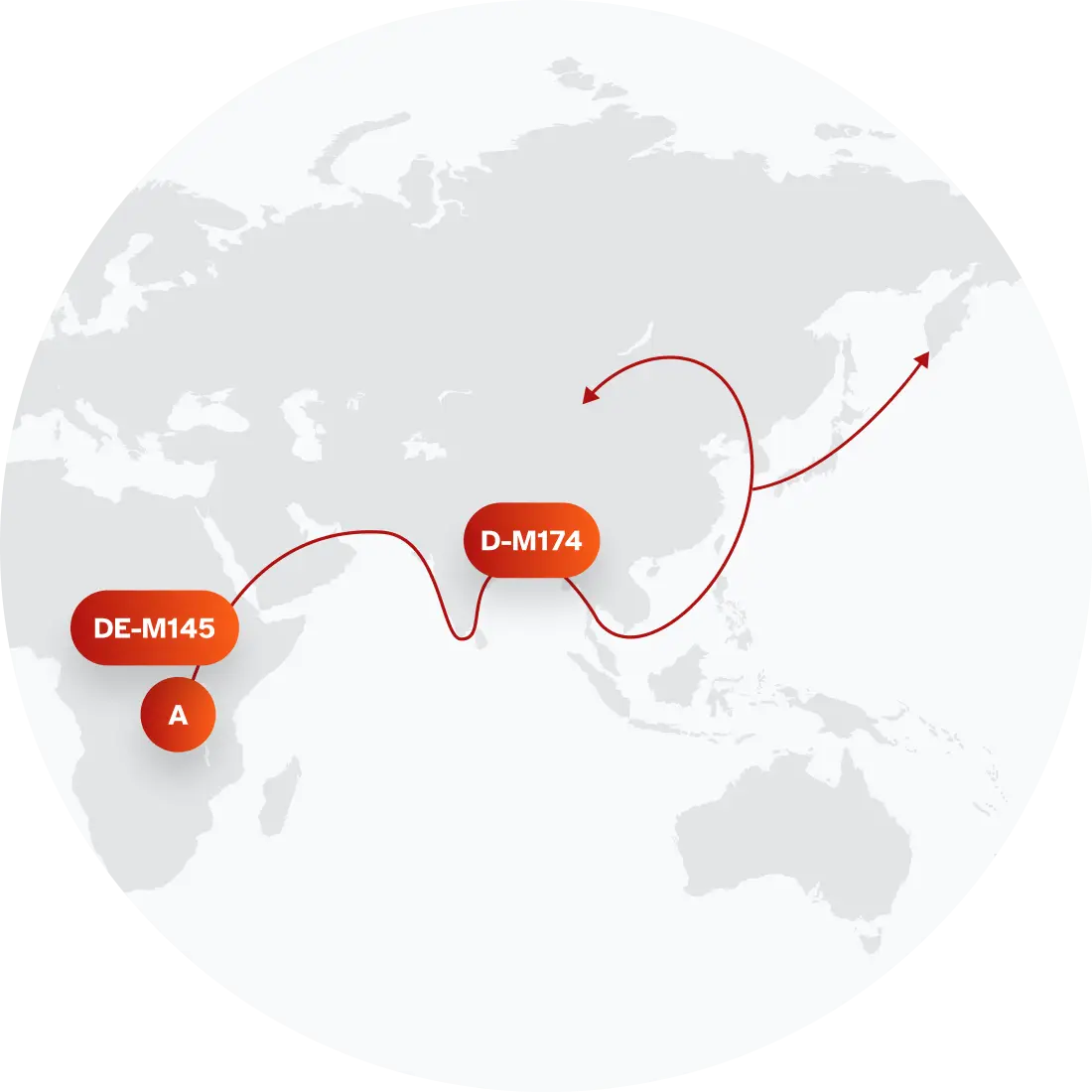 Paternal Haplogroup Origins D-M174
Paternal Haplogroup Origins D-M174
Your paternal lineage may be linked to the ancient Jōmon people of Japan
Haplogroup D-M125 is a branch of D that arose over 12,000 ago, and was likely carried into Japan with the initial wave of migrants. Who were these first men to walk across the land bridge to Japan? Today, we call them the Jōmon. For thousands of years, the Jōmon lived by fishing, hunting and gathering the rich resources of the islands. They also left behind distinctive coiled pottery. In fact, their pottery was some of first in the world!Meanwhile rice agriculture was making quite an impression in mainland China and soon spread throughout eastern Asia. These rice agriculturalists arrived in Japan about 2,300 years ago, quickly taking over many parts of the archipelago. As they introduced new paternal lines, haplogroup D-M55 appears to have been mostly replaced. It did, however, survive in the descendants of the Jōmon in more isolated areas of Japan, including Hokkaido in the north and Okinawa in the south.
Your maternal lineage may be linked to Marie Antoinette
Because it is so dominant in the general European population, haplogroup H also appears quite frequently in the continent's royal houses. Marie Antoinette, an Austrian Hapsburg who married into the French royal family, inherited the haplogroup from her maternal ancestors. So did Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh, whose recorded genealogy traces his female line to Bavaria. Scientists also discovered that famed 16th century astronomer Nicolaus Copernicus traced his maternal lineages to haplogroup H.

What do people with the surname Watanabe have in common?
Spoiler alert: it's complicated. People with the same last name are usually no more genetically similar than a randomly sampled group of people from the same population. That said, people with the same surname are more likely to have similar ancestries than randomly sampled individuals. The reason is the tendency of people with similar cultural or geographical backgrounds to preferentially mate with one another. That's why people who share a surname may be more likely to share traits and tendencies in common than people within the general population. Check out the percentages below to see the prevalences of tastes, habits, and traits of people with your surname compared with prevalences among 23andMe users.
Preferences
Traits
Habits
Wellness
Are health conditions linked to the last name Watanabe?
The short answer is that, if there is an association between surname and health, it's usually more about your ancestry than your name. Individuals with a given surname are no more genetically similar than the general population but often have similar ancestries. The populations of people associated with those shared ancestries often have sets of genetic variations, also known as alleles, in common. Some of those alleles are associated with a greater likelihood of developing certain diseases.
Disease variant frequency by ancestry
Disease allele frequencies in populations associated with the surname Watanabe are shown below. Important Note: not everyone with a disease allele will develop these health condition