Explore the Family Name Shorter
How common is the last name Shorter in the United States?
Based on the Decennial U.S. Census data, the surname 'Shorter' has seen a slight decrease in popularity between 2000 and 2010. In 2000, it was ranked 4,014th most common name, but by 2010 it had slipped to 4,092nd. However, despite this decline in rank, the actual number of people with the Shorter surname increased by 6.81%, from 8,122 in 2000 to 8,675 in 2010. This indicates that while the name became less popular relative to other surnames, more people were named Shorter overall.
| 2000 | 2010 | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | #4,014 | #4,092 | -1.94% |
| Count | 8,122 | 8,675 | 6.81% |
| Proportion per 100k | 3.01 | 2.94 | -2.33% |
Race and Ethnicity of people with the last name Shorter
In terms of ethnic identity, the Decennial U.S. Census data reveals some shifts over the decade. The percentage of Shorters identifying as Black increased slightly from 56.57% to 58.16%. There was also a significant increase in those identifying as Hispanic, jumping from 0.91% to 1.95%. The percentage identifying as White decreased from 39.45% to 35.94%. Other increases were seen among those identifying with two or more races (from 2.20% to 2.97%) and American Indian and Alaskan Native (from 0.43% to 0.54%). The Asian/Pacific Islander category saw a minor increase, rising from 0.43% to 0.44%.
| 2000 | 2010 | Change | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Black | 56.57% | 58.16% | 2.81% |
| White | 39.45% | 35.94% | -8.9% |
| Two or More Races | 2.2% | 2.97% | 35% |
| Hispanic | 0.91% | 1.95% | 114.29% |
| American Indian and Alaskan Native | 0.43% | 0.54% | 25.58% |
| Asian/Pacific Islander | 0.43% | 0.44% | 2.33% |
Shorter ancestry composition
23andMe computes an ancestry breakdown for each customer. People may have ancestry from just one population or they may have ancestry from several populations. The most commonly-observed ancestry found in people with the surname Shorter is British & Irish, which comprises 43.4% of all ancestry found in people with the surname. The next two most common ancestries are French & German (16.5%) and Nigerian (15.1%). Additional ancestries include Ghanaian, Liberian & Sierra Leonean, Angolan & Congolese, Senegambian & Guinean, Eastern European, and Spanish & Portuguese.
Ready to learn more about your ancestry? Get the most comprehensive ancestry breakdown on the market by taking our DNA test. Shop 23andMe
| ANCESTRY BREAKDOWN | COMPOSITION |
|---|---|
| British & Irish | 43.4% |
| French & German | 16.5% |
| Nigerian | 15.1% |
| Other | 24.9% |
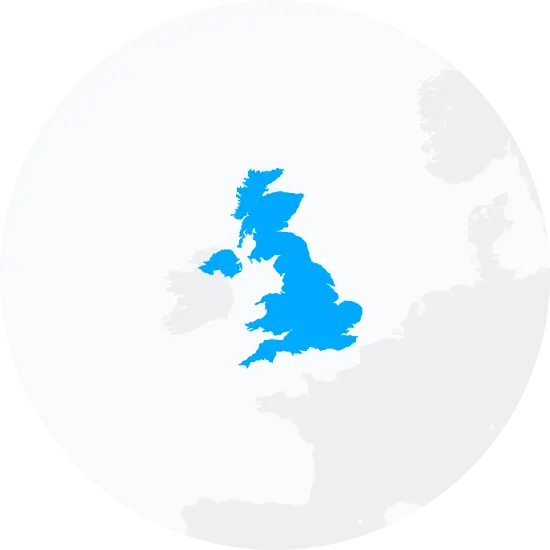
Possible origins of the surname Shorter
Your DNA provides clues about where your recent ancestors may have lived. Having many distant relatives in the same location suggests that you may all share common ancestry there. Locations with many distant relatives can also be places where people have migrated recently, such as large cities. If a large number of individuals who share your surname have distant relatives in a specific area, it could indicate a connection between your surname and that location, stemming from either recent ancestral ties or migration.
Based on 23andMe data, people with last name Shorter have recent ancestry locations all within the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
| RECENT ANCESTRY Location | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Glasgow City, United Kingdom | 69.10% |
| Merseyside, United Kingdom | 69.10% |
| Lancashire, United Kingdom | 69.10% |
| Greater Manchester, United Kingdom | 69.10% |
| Greater London, United Kingdom | 69.10% |
What Shorter haplogroups can tell you
Haplogroups are genetic population groups that share a common ancestor on either your paternal or maternal line. These paternal and maternal haplogroups shed light on your genetic ancestry and help tell the story of your family.
The top paternal haplogroup of people with the surname Shorter is R-S660, which is predominantly found among people with European ancestry. Haplogroup R-S660 is descended from haplogroup R-M343. Other common haplogroups include E-P252 and I-M253, which are predominantly found among people with Sub-Saharan African and European ancestry. Other surnames with similar common haplogroups are: Gilmore, Arrington, Quinn, Buckner, Greer, Mcfadden, Guinn, Egan, Meredith, Mullins.
The most common maternal haplogroups of people with Shorter surname are: H1, H, L2a1. These most commonly trace back to individuals of European and Sub-Saharan African ancestry.
 Paternal Haplogroup Origins R-M343
Paternal Haplogroup Origins R-M343
Your paternal lineage may be linked to Niall of the Nine Hostages
The spread of haplogroup R-M222 in northern Ireland and Scotland was likely aided by men like Niall of the Nine Hostages. Perhaps more myth than man, Niall is said to have been a King of Tara in northwestern Ireland in the late 4th century C.E. His name comes from a tale of nine hostages that he held from the regions he ruled over. Though the legendary stories of his life may have been invented hundreds of years after he died, genetic evidence suggests that the Uí Néill dynasty, whose name means "descendants of Niall," did in fact trace back to just one man who likely bore haplogroup R-M222, a branch of R-M269.The Uí Néill ruled to various degrees as kings of Ireland from the 7th to the 11th century C.E. In the highly patriarchal society of medieval Ireland, their status allowed them to have outsized numbers of children and spread their paternal lineage each generation. In fact, researchers have estimated that between 2 and 3 million men with roots in north-west Ireland are paternal-line descendants of Niall.
Your maternal lineage may be linked to the nomadic Tuareg of the Sahara
Though haplogroup H1 rarely reaches high frequencies beyond western Europe, over 60% of eastern Tuareg in Libya belong to haplogroup H1. The Tuareg call themselves the Imazghan, meaning “free people.” They are an isolated, semi-nomadic people who inhabit the West-Central Sahara and are known today for a distinctive dark blue turban worn by the men, and for their long history as gatekeepers of the desert.How did women carrying H1 make it all the way from western Europe to this isolated community? They likely migrated from Spain across the Strait of Gibraltar into Morocco after the Last Ice Age, where they were assimilated into the Berbers of the Mediterranean coast. Then, about 5,000 years ago, the Sahara shifted from a period of relative habitable conditions to its dramatically arid desert environment. This shift may have caused migrations throughout the Sahara, prompting the ancient Tuaregs to meet and mingle with the Berbers, bringing H1 lineages into their population.

What do people with the surname Shorter have in common?
Spoiler alert: it's complicated. People with the same last name are usually no more genetically similar than a randomly sampled group of people from the same population. That said, people with the same surname are more likely to have similar ancestries than randomly sampled individuals. The reason is the tendency of people with similar cultural or geographical backgrounds to preferentially mate with one another. That's why people who share a surname may be more likely to share traits and tendencies in common than people within the general population. Check out the percentages below to see the prevalences of tastes, habits, and traits of people with your surname compared with prevalences among 23andMe users.
Preferences
Traits
Habits
Wellness
Are health conditions linked to the last name Shorter?
The short answer is that, if there is an association between surname and health, it's usually more about your ancestry than your name. Individuals with a given surname are no more genetically similar than the general population but often have similar ancestries. The populations of people associated with those shared ancestries often have sets of genetic variations, also known as alleles, in common. Some of those alleles are associated with a greater likelihood of developing certain diseases.
Disease variant frequency by ancestry
Disease allele frequencies in populations associated with the surname Shorter are shown below. Important Note: not everyone with a disease allele will develop these health condition